Cyber threats such as ransomware attacks have become more sophisticated, necessitating advanced strategies for data protection. One such strategy is the use of immutable snapshots. These snapshots, which capture the state of your data at a specific point in time, and are unalterable, play a crucial role in protecting your critical information from unauthorized alterations and malicious cyber-threats such as ransomware attacks, malware, viruses, and hackers.
The Necessity of Immutable Snapshots for Data Protection
Unlike traditional snapshots that can be modified or deleted, immutable snapshots are designed to be impervious to any form of tampering. This immutability ensures that once a snapshot is created, it remains unaltered and serves as an authentic reference point for data recovery.
This ability to provide a “snapshot in time” can prove invaluable in recovering data to a known, uncorrupted state after an attack.
In modern IT landscapes, where data is constantly under the threat of cybercriminals and system glitches, the implementation of immutable snapshots has become a cornerstone of data protection strategies. These snapshots work as a safeguard against unauthorized changes, ransomware attacks, and accidental deletions.
By providing a secure and unalterable copy of your data, immutable snapshots grant organizations the confidence to maintain data integrity and rapidly recover from disruptions.
As we delve deeper into the realm of immutable snapshots, we’ll explore their benefits, use-cases, and best practices for effective implementation.
Understanding Immutable Snapshots
In the realm of data protection, understanding the mechanics and benefits of immutable snapshots is fundamental. These snapshots, often referred to as “read-only” snapshots, are a critical feature in modern IT environments.
Let’s delve into their inner workings and explore the advantages they bring to the table.
Explaining How Immutable Snapshots Work
Immutable snapshots fundamentally alter the snapshot creation process to ensure data integrity. Unlike traditional snapshots that can be modified or overwritten, immutable snapshots are designed to be unchangeable once created. This is achieved through a mechanism that locks down the snapshot, rendering it impervious to any alterations, whether accidental or intentional.
When an immutable snapshot is generated, the system creates a cryptographic hash value for the data being captured. This hash is then securely stored alongside the snapshot. Subsequent attempts to alter the data result in a hash mismatch, signaling that the data has been tampered with. This failsafe mechanism provides an additional layer of protection against ransomware attacks, malware intrusions, and unauthorized modifications.
Key Advantages and Role in Enhancing Data Security
The role of immutable snapshots in data security cannot be overstated. These snapshots offer several crucial advantages that contribute to the enhancement of overall data protection:
- Ransomware Resilience: Immutable snapshots serve as a safeguard against ransomware attacks. In the event of an attack, where the attacker demands a ransom for data release, organizations can confidently recover from uncorrupted snapshots without yielding to the ransom demand.
- Data Recoverability: With immutable snapshots, organizations have a reliable reference point to restore data to a known, secure state. This is invaluable when dealing with accidental deletions, system failures, or data corruption.
- Compliance and Audit: Immutable snapshots play a pivotal role in ensuring data compliance. Sectors such as healthcare, finance, and legal services can benefit from snapshots that are impervious to unauthorized changes, thus maintaining regulatory compliance.
- Preservation of Historical Data: Immutable snapshots provide a historical view of data over time. This can be invaluable for auditing purposes, historical analysis, and meeting legal retention requirements.
- Data Immutability: The inability to modify immutable snapshots safeguards data from internal or accidental changes, bolstering data reliability and authenticity.
Use-Cases of Immutable Snapshots
Reliable Disaster Recovery and Quick Data Restoration
Immutable snapshots play a crucial role in ensuring reliable disaster recovery and swift data restoration in the face of unexpected data loss or system failures. By creating immutable copies of data at specific points in time, organizations can establish a solid foundation for recovery strategies.
In the event of a data breach, ransomware attack, or accidental deletion, these snapshots serve as unaltered versions of data that can be swiftly restored to bring systems back online without compromising data integrity.
Immutable snapshots provide a powerful mechanism for reverting systems to a secure state before an incident occurred, minimizing downtime and potential financial losses. These snapshots act as a safety net, safeguarding against a wide array of data loss scenarios, including cyberattacks, hardware failures, and human errors.
Ensuring Long-Term Data Retention and Archiving
Immutable snapshots provide a secure and efficient solution for ensuring long-term data retention and archival needs.
In industries with stringent compliance regulations and data retention requirements, such as finance and healthcare, organizations must retain data for extended periods while maintaining its integrity. Immutable snapshots create point-in-time copies of data that cannot be modified or tampered with, making them ideal for meeting regulatory mandates.
By leveraging immutable snapshots, organizations can confidently store historical data, records, and archives, knowing that these copies are unalterable. This capability ensures that data remains intact and unchangeable, regardless of the passage of time.
Immutable snapshots simplify the process of compliance and auditing, allowing organizations to demonstrate their adherence to data retention regulations.
Supporting DevOps and Testing Environments
Immutable snapshots offer valuable support for DevOps and testing environments by providing a stable and consistent dataset for development and testing activities. In these environments, data consistency and reliability are critical to ensure accurate results and efficient development cycles. Immutable snapshots capture a specific state of data, making it an excellent resource for creating consistent testing scenarios.
Developers and testers can use immutable snapshots to create isolated environments that replicate production data without the risk of modifications. This ensures that testing outcomes accurately reflect real-world conditions, leading to higher-quality software releases.
Additionally, these snapshots can be easily rolled back after testing, eliminating the need for time-consuming data provisioning processes.
How to Set Up Immutable Snapshots for Network Attached Storage (NAS) Repositories
Before you can setup immutable snapshots you will need the StoneFusion™ for Baremetal or Storage Concentrator Virtual Machine (SCVM™) installed on VMware, Hyper-V, KVM, Citrix (XenServer), or StoneFly Persepolis.
To set up immutable snapshots for NAS repositories, we need to first set up a NAS repository.
First, let’s create a NAS segment. Navigate to the NAS tab, select Volumes, then Segment, and click on Segment Create.
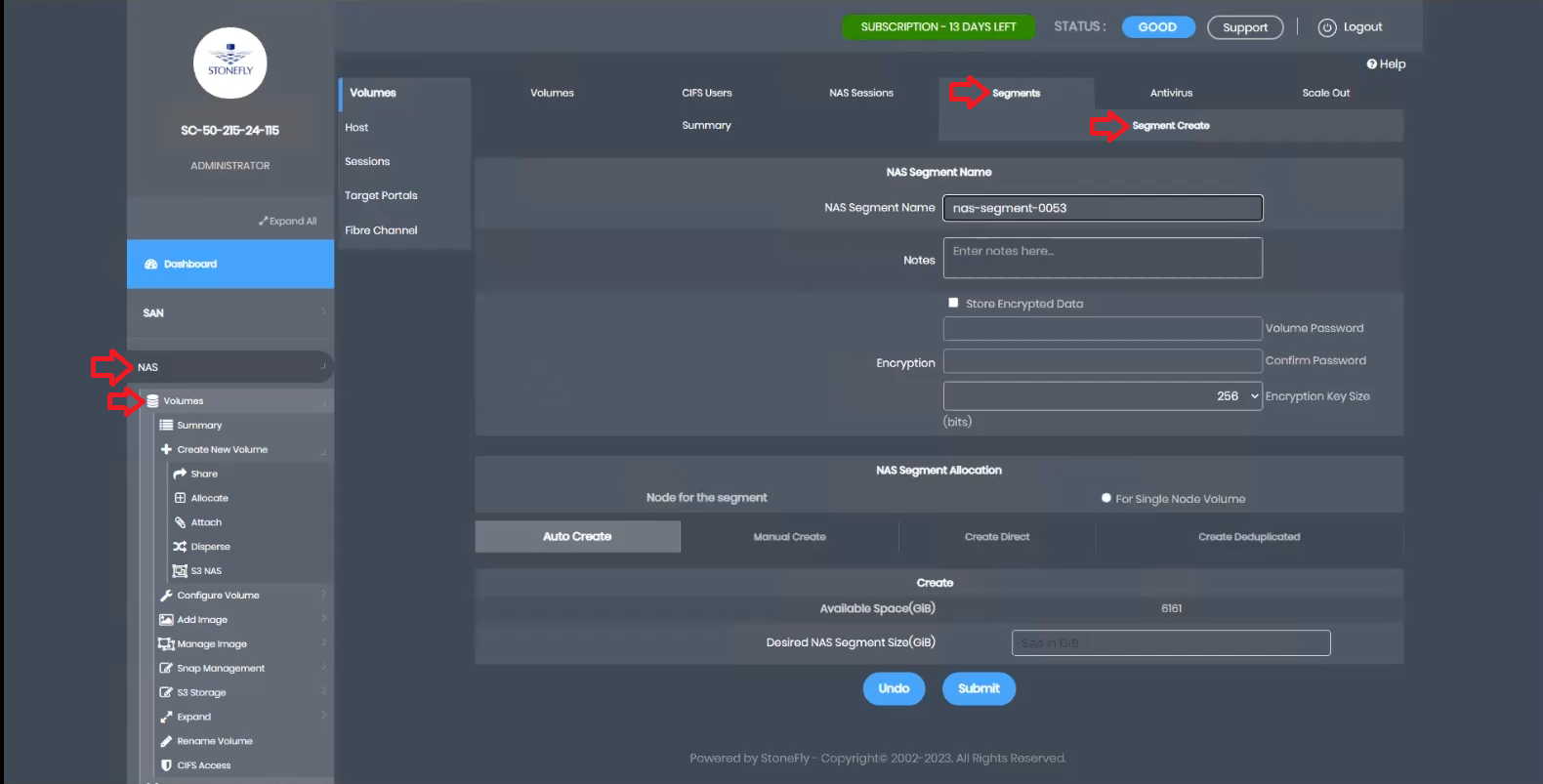
Provide a name for the segment, choose Manual Create, allocate the desired capacity, and click submit.
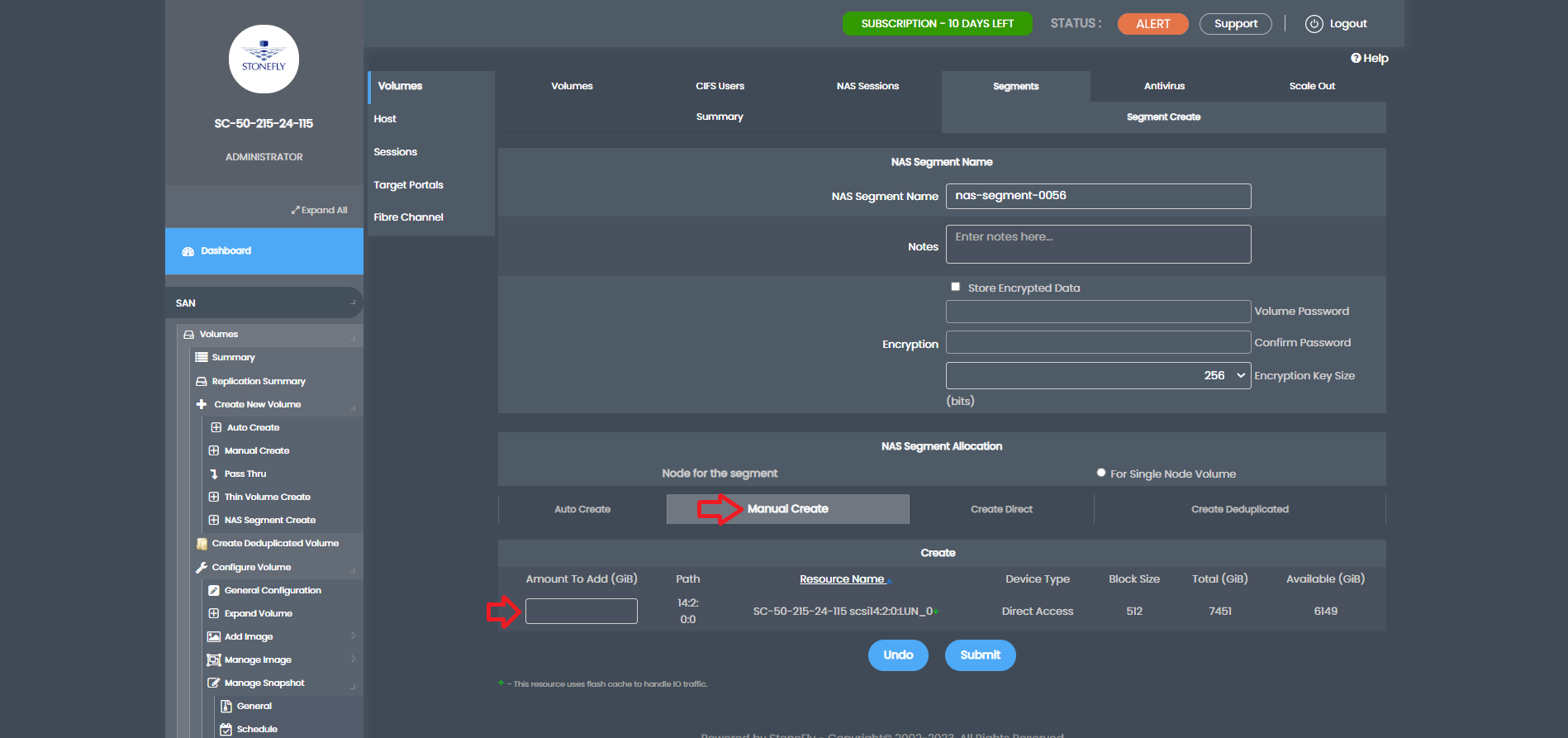
Once the NAS segment is created, we can proceed to create a NAS volume. In the NAS volume creation section, specify a name for the volume, choose whether to export it via CIFS or NFS (both supported for immutable snapshots), and click submit.
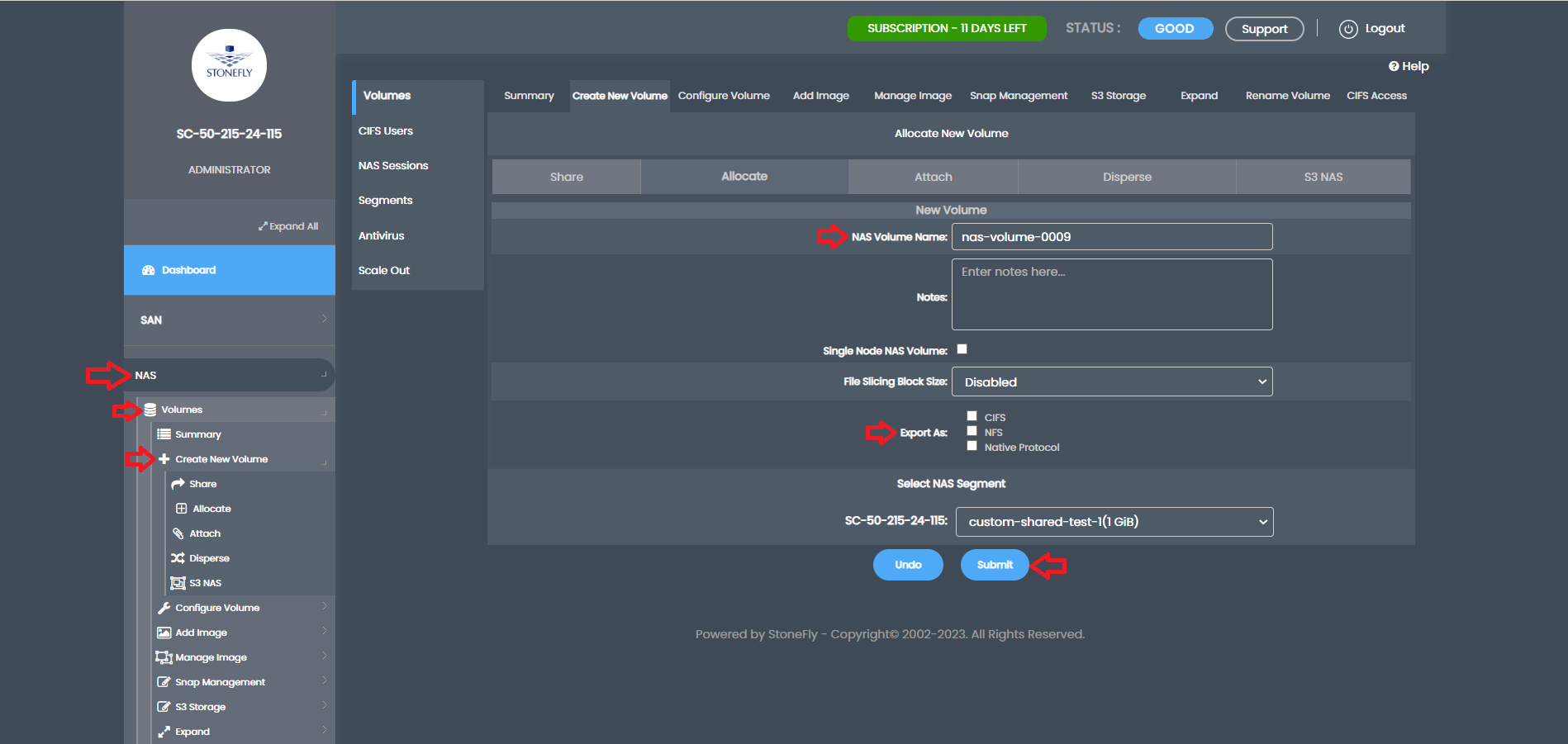
After the NAS volume is created, the next step is to create snapspace for it. Go to the SAN tab, select Volumes, Configure Volumes, Manage Snapshot, and click on General. From the drop-down, select the newly created NAS volume and click Create Snapspace.
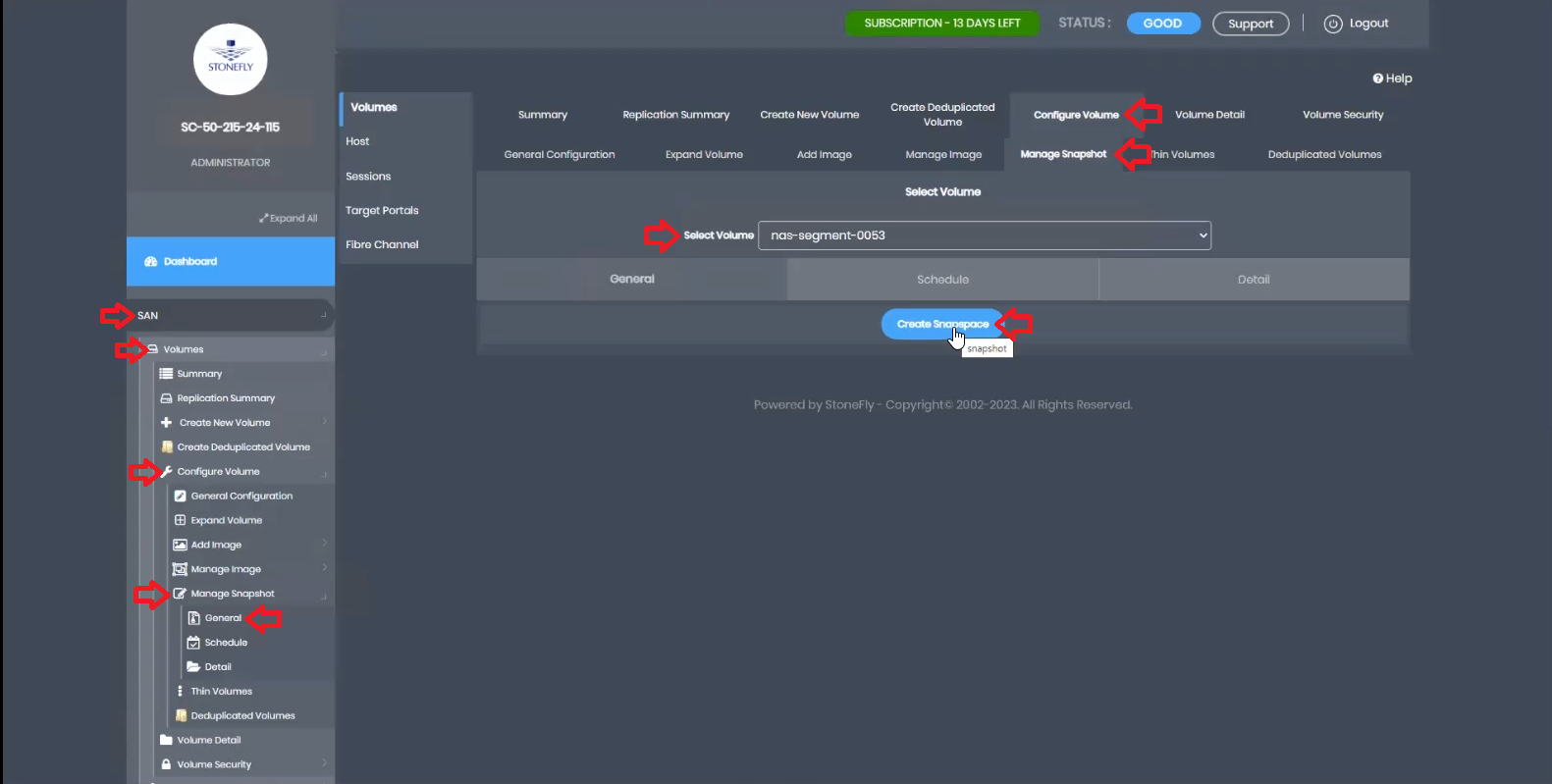
Here, you can designate the capacity for snapshots. It is recommended to allocate at least 20% of the NAS volume size, or more, depending on the change rate. After allocating the size, click submit.
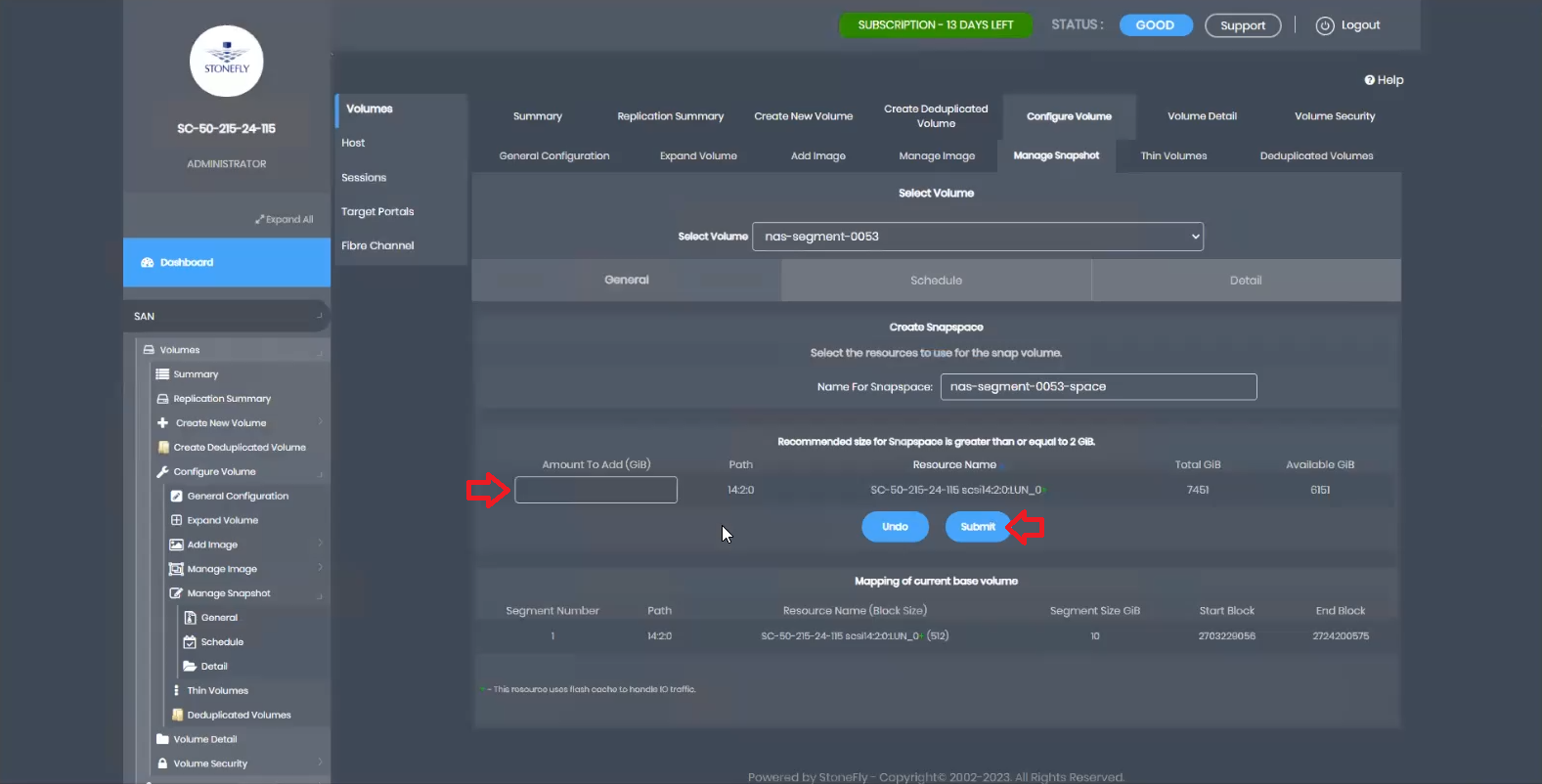
In the event of snapspace running out of space, you can manually expand it or configure the system’s behavior automatically. Choose between preserving the live volume or preserving the snapshot.
Preserving the live volume allows writing to the volume but prevents taking snapshots until snapspace is manually expanded. Preserving the snapshot discontinues writes to the volume, locking it down.
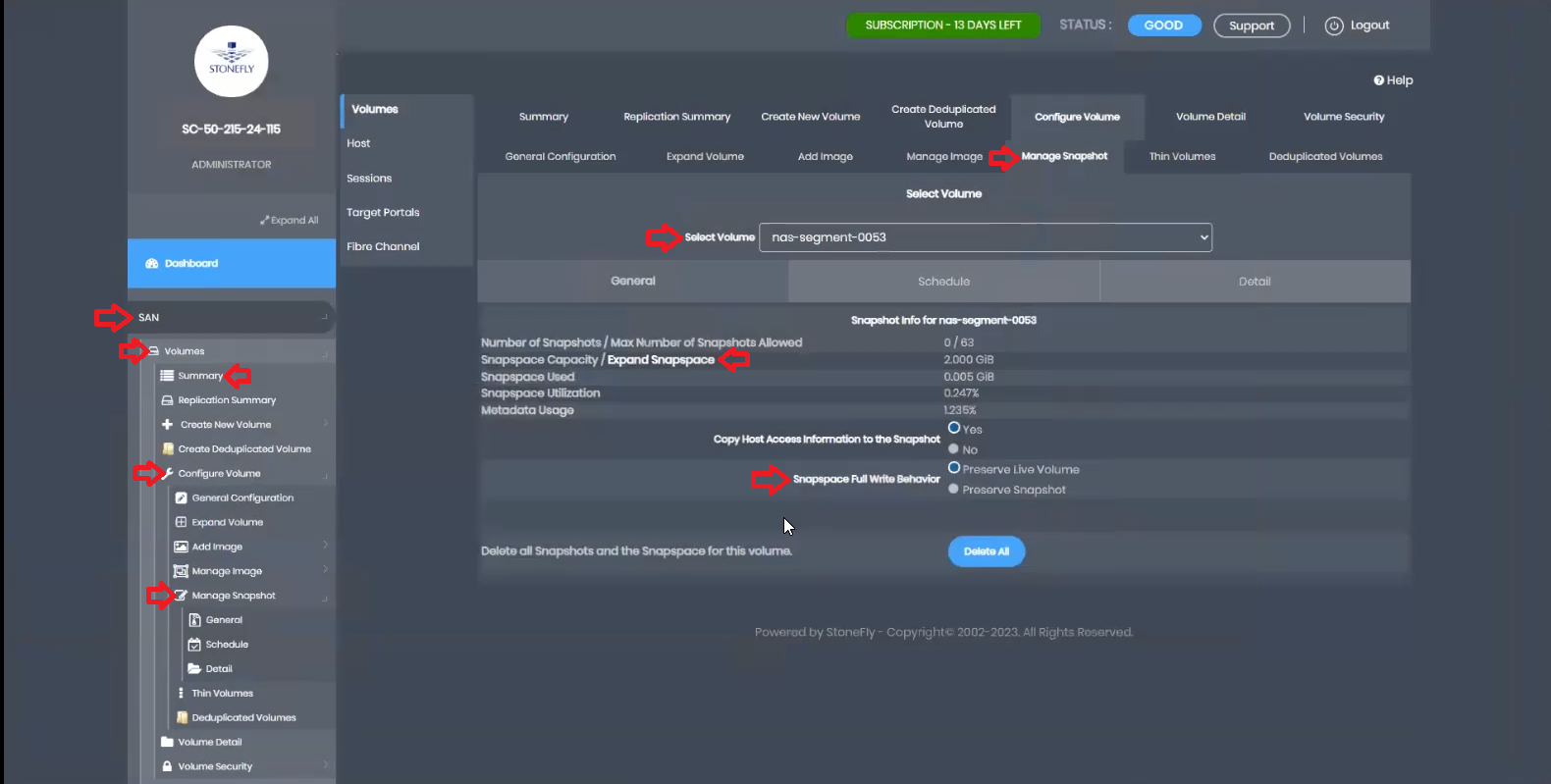
Now, let’s proceed to create the snapshots. Go back to the NAS tab, select Volumes, and then Summary. Click on Snap Management from the top tabs. Choose the newly created volume from the drop-down and click Enable Snapshots.
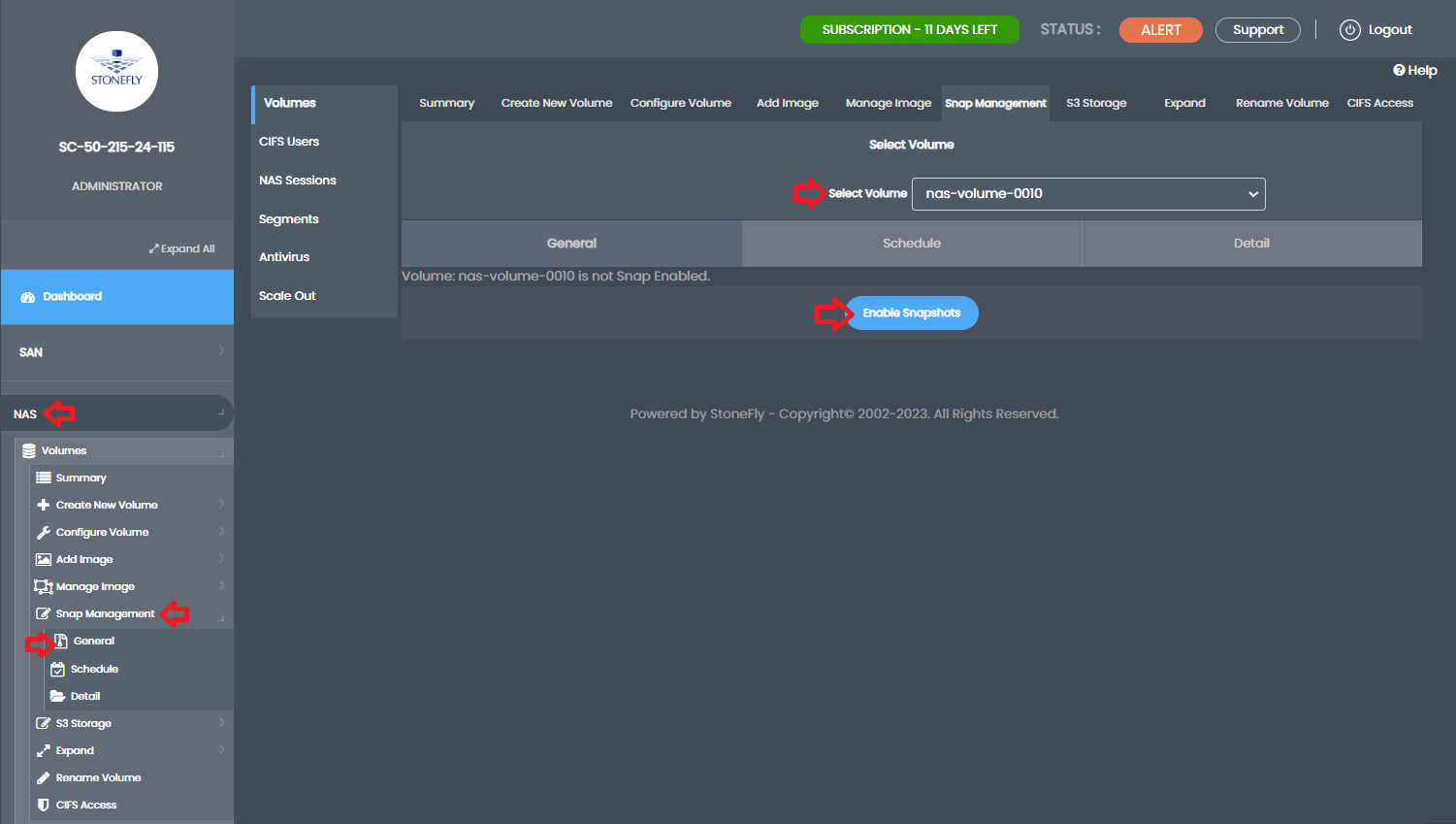
In the General tab, you can immediately take a manual snapshot if needed. Set the Snapspace Full Write behavior as discussed earlier. In the Schedule tab, you have the flexibility to schedule monthly, weekly, daily, or hourly cycles according to your requirements. The system allows for granular control over the timing and retention of snapshots.
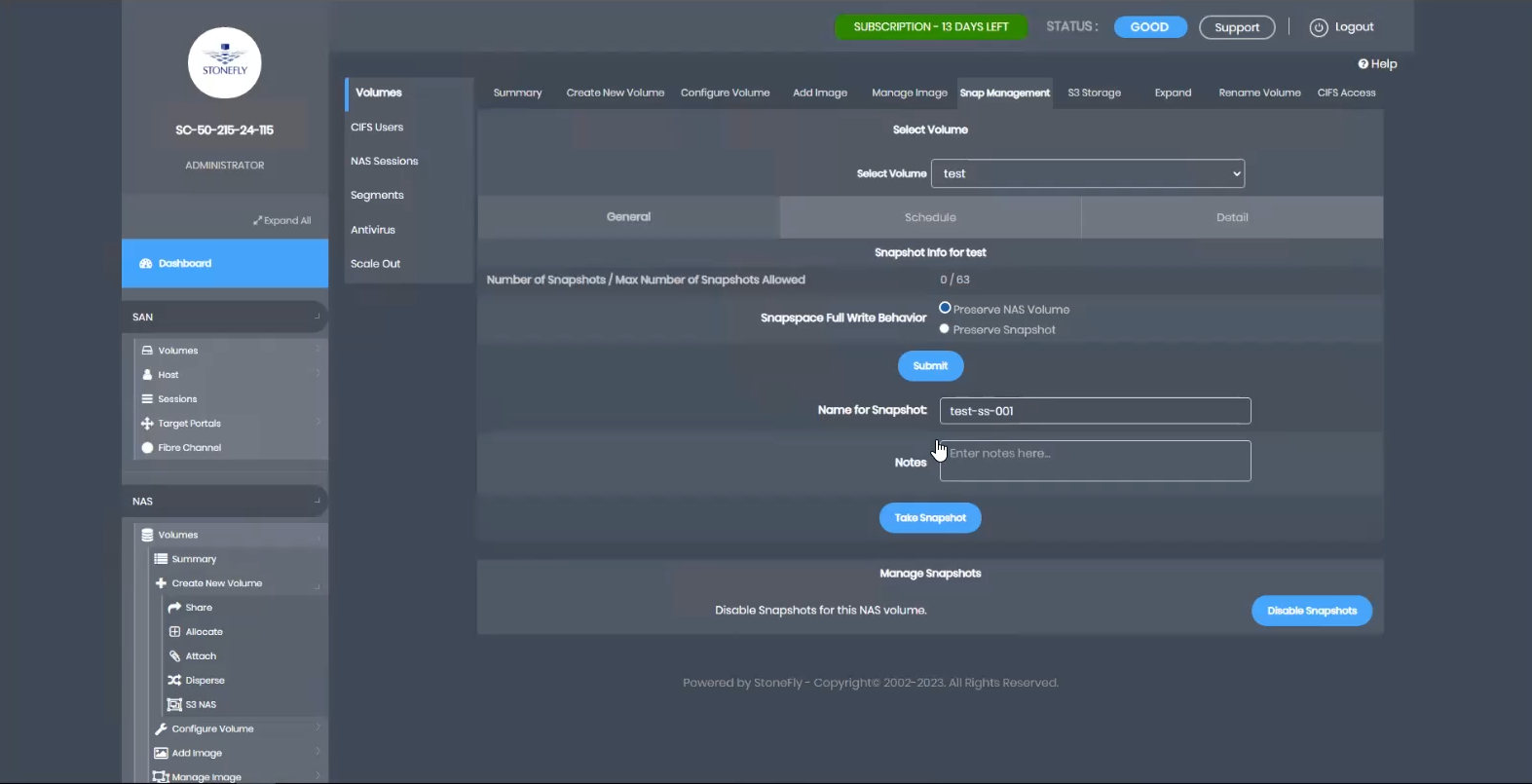
In the Details tab, you will find a list of all the snapshots. Since we just created the volume in this example, there are no snapshots yet. Let’s create one manually by providing a snapshot name and clicking Take Snapshot. Confirm when prompted. The snapshot count will update accordingly.
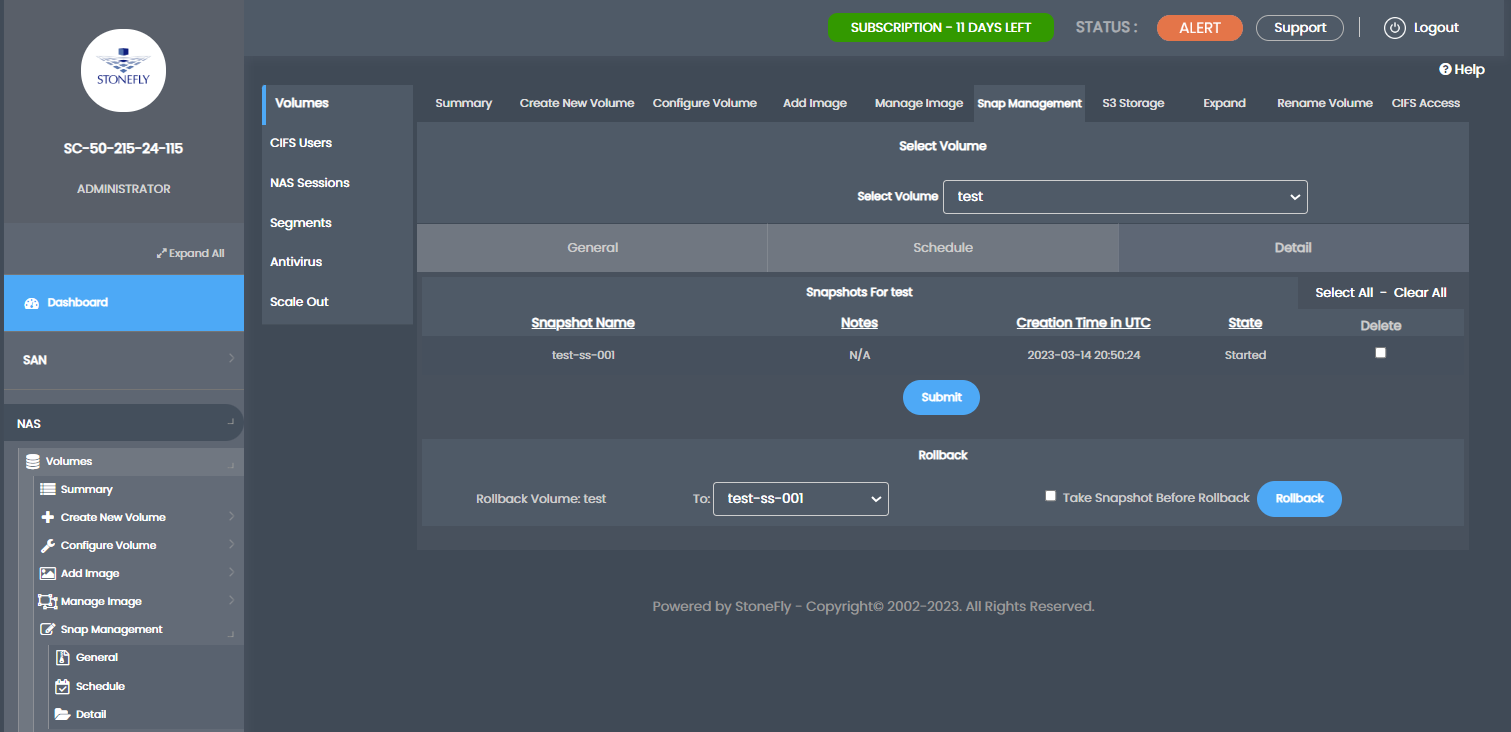
It’s important to note that accessing a snapshot volume for file recovery or volume restoration follows the same UNC path as the original volume, with the addition of a leading slash followed by the snapshot name. Users need the name of the specific snapshot from the administrator. As long as they have access to the original volume, they will also have access to its snapshots.
Remember that snapshots are immutable, meaning users can only read and restore from them. Modifying or deleting snapshots during the retention period is not possible.
StoneFusion allows for a maximum of 64 snapshots per volume and a total of 8 snap-enabled volumes per appliance. These limits can be adjusted based on the change-rate and client preferences, considering the available system resources.
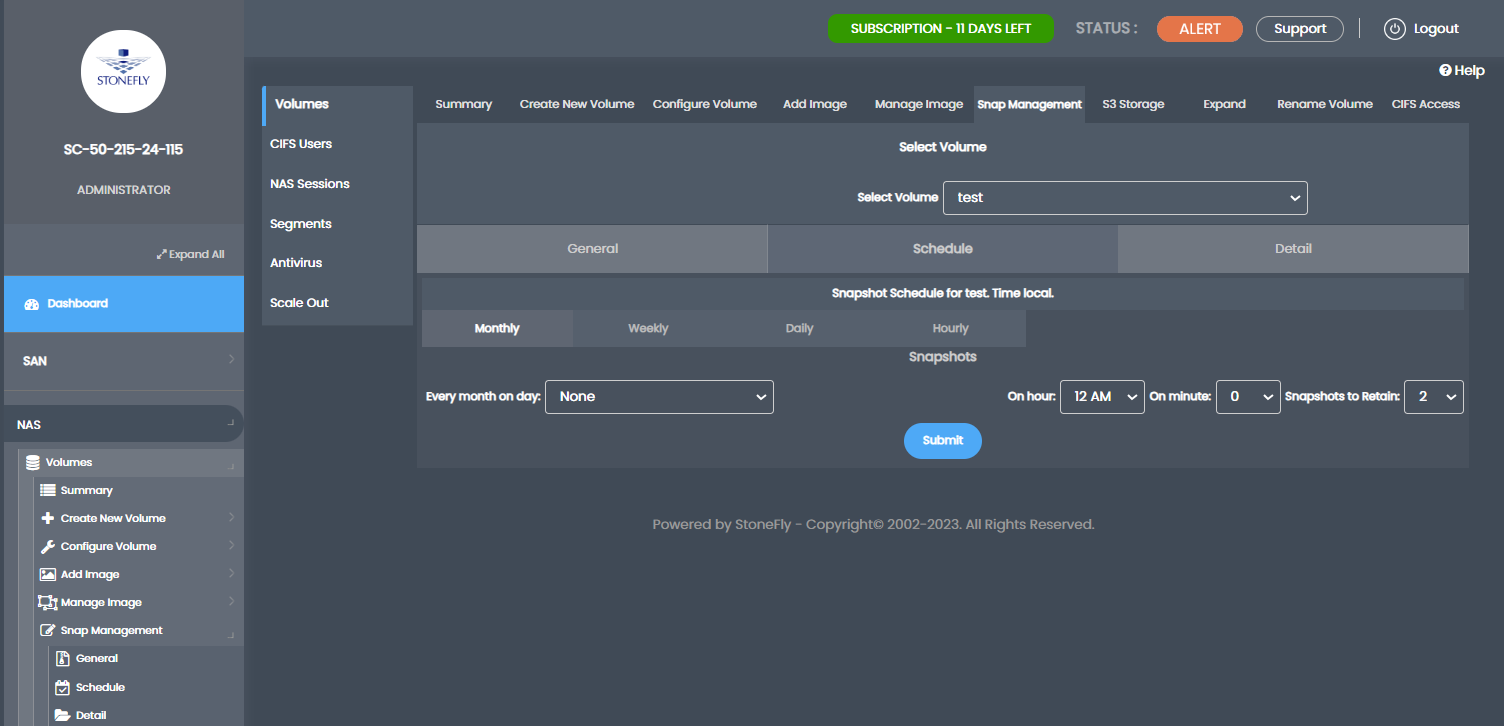
In the Schedule Tab, you can schedule hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly snapshots.
Furthermore, an optional Veeam agent is available within StoneFusion, allowing administrators to configure virtually unlimited incremental backups as required. The Veeam agent operates independently, utilizing its own change block tracking system and running locally on the appliance for faster backups with minimal latency. Alternatively, the Veeam agent can be installed on a network-connected appliance if desired.
Best Practices for Maximizing Immutable Snapshots
Immutable snapshots offer robust data protection, but their effectiveness depends on proper implementation and management. By following best practices, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure, unalterable, and easily recoverable.
Efficient Snapshot Scheduling and Retention Policies
Implementing an effective snapshot scheduling strategy is crucial to ensure that critical data is captured at regular intervals. Organizations should determine the appropriate frequency of snapshots based on their data’s volatility and importance. Additionally, defining retention policies is essential to manage storage usage effectively.
By establishing clear guidelines for snapshot creation and retention, organizations can strike a balance between data protection and storage efficiency. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these policies ensures that the right data is retained for the necessary duration while minimizing unnecessary storage costs.
Isolating Snapshots through Air-Gapping
Air-gapping involves isolating snapshots from the primary network or storage infrastructure, adding an extra layer of security against cyber threats. By storing immutable snapshots in a separate, isolated environment, organizations create a safeguard against unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Air-gapped snapshots provide a reliable restore point even in the face of ransomware attacks or data breaches. This approach prevents attackers from altering or deleting snapshots, ensuring data integrity remains intact.
Enhancing Security Layers for Optimal Protection
Implementing a multi-layered security approach further enhances the protection of immutable snapshots. Organizations should consider combining techniques such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection to fortify the security of snapshot repositories.
Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data within the snapshots remains unreadable. Access controls limit who can interact with snapshots, minimizing the risk of accidental modifications. Intrusion detection systems continuously monitor snapshot activities for any suspicious behavior, allowing for prompt action in case of potential threats.
Monitoring and Auditing Immutable Snapshot Activities
Regularly monitoring and auditing snapshot activities is essential to maintain a clear understanding of how data is being protected and accessed. By keeping track of snapshot creation, modification, and restoration, organizations can detect any anomalies or unauthorized actions promptly.
Monitoring and auditing provide visibility into the snapshot lifecycle, enabling organizations to identify potential issues and ensure compliance with data protection policies. This practice not only enhances data security but also facilitates better management of snapshots and their associated resources.
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving digital landscape, embracing immutable snapshots is crucial for robust data security. From thwarting ransomware to meeting compliance, these snapshots ensure data integrity. By following best practices like efficient scheduling, air-gapping, and layered security, organizations can harness the power of immutable snapshots to fortify their data protection efforts.